Published on September 29th 2024 | 6 mins , 1135 words
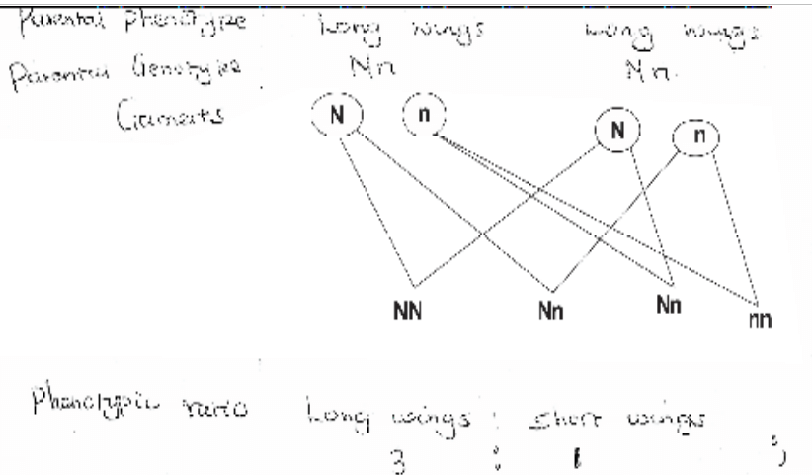
1. In an Experiment, Drosophila (Fruit flies) with long wings were crossed with those having vestigial (short wings).
All the offspring (F1 generation) from this cross had long wings.
Using letter N to denote the gene for wing size:
(a) Give the genotypes of the parents; (2marks)
NN: nn:
(b) Work out the phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation if the F1 generation was selfed. (5marks)
(c) The gene for eye colour in Drosophila is located on the X-chromosome. What name is given to such genes?
- Sex- Linked
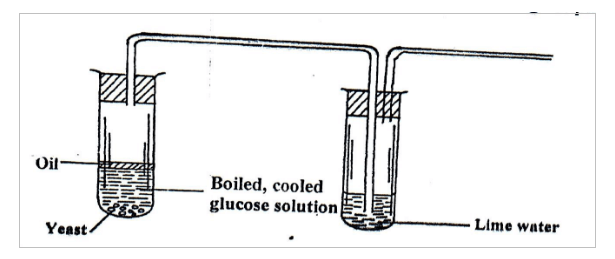
2. A class set up the experiment below to investigate a certain biological process.
(a) Name the process under investigation (1mark)
Anaerobic respiration / fermentation rej respiration alone.
(b) Why was the glucose solution oiled and then coiled before the yeast was
added? (2marks)
- Boiled to expel air/ Oxygen in solution; coiled to prevent killing /Denaturing of yeast cells.
(c) (i) What is the role of yeast in the experiment?
- Yeast has enzyme to break down glucose.
(ii) Name two products in the experiment
Ethanol; Carbon IV oxide; heat (any 2)
3. a) State the functions of the following cell organelles
(i) Centriole (1mark)
- Formation of Celia and Flagella.
- Used in cell division in formation of spindle fibre
(ii) Lysosome
- Contains lytic enzymes which digest and destroy worn out organelles cells
(b) What is the meaning of the term resolving power as used in microscopy? (1mark)
- Ability/capacity to distinguish between two structures that look very similar
(c) Give two roles of Active transport in plants. (2 marks)
- Transportation of manufactured food in the phloem
- Absorption of mineral salts by root hairs.
d) Explain why human red blood cells burst when placed in distilled water. (3marks)
Water is hypotonic to content of red blood cell: water molecules / hemolysis entered unto red blood cell by osmosis hence swell and burst due to weak cell membranes.
4. Study the diagram below and answer the following questions.
(a) Name the muscles labeled A and B. (2marks)
- Biceps
- B-Triceps
(b) What happens to each muscle as the arm is straightened?
- A-Biceps relax B-Triceps Contract
(c) Name Joint at C.
- Hinge Joints
(d) (i) Some Herbaceous stems have very little strengthening tissue yet still
remain upright. Explain (2 marks)
- They have Parenchyma cells / tissues which absorbs water and
become turgid
(ii) Name the strengthening material in sclerenchyma tissue (1mark)
- Lignin
5. Below is a diagram of plant a form three student completed while carrying out an ecological study?
(a) With reasons identify the division into which the students classified the plant. (1mark)
Division Pteridophytes
Reasons Precise of compound leaves with leaflets known as pinna.
b) (i) Name the structure that produces spores in this plant (1 mark)
ii) State two differences between the plant above and those belonging to the phylum
Spermatophyte.
Pteridophgta spermatophyte (2marks)
Non flowering Bears Flowers
Has rhizomes/ lack Have roots
Lack distinct stem Have distinct stems
(c) State the features of this plant that made the student classify it in the kingdom of Plantae.
- Body is differentiated into leaves, stem, and roots.
- Shows alteration of generation
- Reproduce by sonication
SECTION B
Answer questions 6 (COMOPULSARY) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
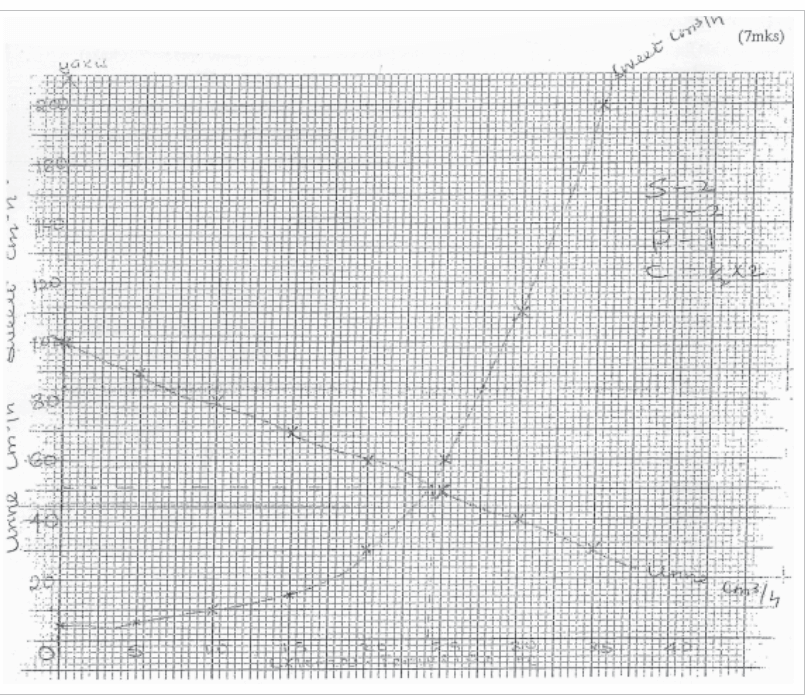
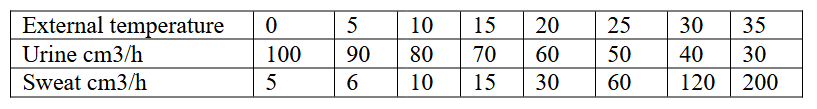
6. The table below shows how the quantities of sweat and Urinary vary with external temperature.
(a) Using the same axes, draw graphs of quantities of urine and seat produced against the external temperature. (7mks)
(b) At what temperature is the amounts of sweat and urine produced equal?
- 24.5 C 0.5 -0.3
(c) Account for the amount of sweat produced as the temperature rises.
- Sweat produced increases with increase in temperature; as the temperature raises vaporization of sweat in which latent heat of vaporization is absorbed from body.
(d) Explain the observation made on the amount of urine produced as temperature rises (4mks)
- Increase in temperature decreases the amount of urine produced because increased sweat increased osmotic potential of blood; more water reabsorbed into blood stream in the Kidney tubules: resulting to production of little and concentrated urine.
(e) Explain how the following help temperature regulation when it’s cold:
(3mks)
- Hair
When its cold erector pull muscles contract hair stands trapping air less heat is lost.
ii) Blood Vessels.
Aerials contract less blood flows near skin surface reducing heat loss by radiation / convection.
7. a) Describe the photosynthetic theory of opening and closing of stomata. (10mks)
b) Describe the regulation of blood sugar level in man (10mks)
7. a) Describe the photosynthetic theory of opening and closing of stomata.
During the day of photosynthesis take place in the guard cells due to presence of light; there is formation of sugar / glucose on the guard cells; accumulation of glucose raise their osmotic pressure; this makes the guard cells to gain water by osmosis from the neighboring epidermal cells; those become targid and bulge ; causing the stomata to open; During the night there is no photosynthesis due to the absence of light; no sugar formation in the guard cell; the osmotic pressure of the guard cells decreases; guard cells lose water by osmosis to the neighbouring epidermis cells they shrink making the stomata to close.
(b) Regulation of blood sugar
When the blood sugar rises ; it is detected by the hyperthasian which stimulate the pancrease; to release insulin through the blood the insulin get to the liver where it stimulates the convention of excess glucose to glycogen and falls which are stored; the insulin also enhances rapid breakdown of glucose in the muscle cell; those events lead to a fall in blood sugar back to normal; when the blood sugar is low ; the hypothalamus stimulates the pancrease to release glucagon which via the blood stream get to the liver where it stimulates the liver to convert glycogen to glucose; there is also less breakdown of glucose in the cells leading to rise in the blood sugar level back to normal.
8. Describe the role of hormones in the human menstrual cycle.
(Anterior or lobe) of pituitary gland secrete follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) FSH causes graffian follicle to develop( in the ovary)’; it also stimulates ovarian tissues /tissue of the ovary/ wall of the follicle to secrete Oestrogen; Oestrogen stimulates (anterior lobe) of pituitary to produce leutenising hormone (LH) causes Ovulation ; it also causes the gracificin follicle to change into corpus / Luteum LH stimulate Leutum to secrete Progesterone; progesterone causes proliferation of uterine wall in preparation for implantation; Oestrogen /progesterone inhibits production of FSH by anterior lobe of pituitary; thus no more follicles develop and oestrogen production reduces in the next two weeks progesterone level rises and inhibit production of LH. Corpus leuteurn stops producing progesterone and menstruation occurs when the level of progesterone drops