Published on May 18th 2024 | 19 mins , 3792 words
KCSE 2023 Geography Paper 2 Marking scheme
1. (a) Name two minerals that occur as weathering products. (2 marks
Ø Diamond
Ø Gold
Ø Platinum
Ø Tin
(b) State three uses of soda ash. (3 marks)
Ø Used in glass and bottle manufacturing industries.
Ø Used in making detergents and soaps.
Ø For petroleum refining and chemical industries.
Ø As a water softener or water treatment.
Ø Used in disulphurising steel.
Ø For paper smoothening in paper making industries.
Ø In manufacture of textiles.
Ø In production of salts
2(a) Name the hydroelectric power projects located in each of the following rivers in Africa:
i) River Zambezi; (1 mark)
Ø Kariba hydroelectric power station
(ii) River Volta. (1 mark)
Ø Akosombo hydroelectric power station
b) State three factors that have hindered the development of solar energy in Kenya. (3 marks)
Ø Presence of other more powerful reliable sources of energy
Ø Relies of foreign technology therefore expensive to install Ø Absence of relevant government policy on solar power
Ø Inadequate financial capital by many Kenyans to invest in solar power
Ø Solar power is unreliable in running heavy machines |
3 3Figure 1 is a map that shows wheat growing areas of Canada. Use it to answer question 3(a).
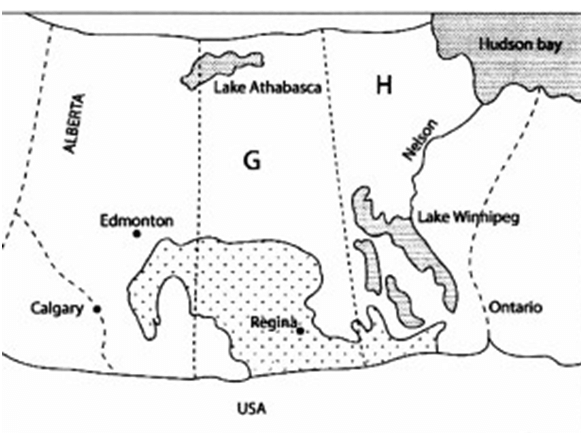
Ø G-Saskatchewan
Ø H-Manitoba
3 (b) State three reasons for the increase in the price of maize in Kenya. (3 marks)
Ø High demand for maize
Ø Low production leading to scarcity
Ø Unscrupulous traders hoarding maize
Ø Government policy in withdrawal of maize subsidy
Ø Politics deciding prices
Ø Maize is stable food therefore few substitutes
Ø Insecurity discouraging even distribution of maize
Ø High cost of fuel making transportation expensive
Ø Impassable roads making some areas inaccessible
4 (a) Explain the term visible trade. (2 marks)
Ø All commercial activities dealing with exchange /selling or buying/ importing/exporting of physical/tangible goods
4 (b) State three economic benefits of Southern African Development Community (SADC) to its member states. (3 marks)
Ø Created integrated committee of ministers to formulate policies
Ø Facilitated transfer of technology across the country
Ø Free movement of Labor across member states curbing shortage of labor boosting production
Ø Has eliminated trade barriers leading to free movement of goods among member states
Ø Providing financial investment on key projects boosting trade
5 (a) Apart from pollution, name two other environmental hazards that occur as a result of human activities. (2 marks) Ø Atomic and gas explosions
Ø Deforestation
Ø Desertification
Ø Drought
Ø Epidemics
Ø Fires/oil tankers
Ø Landslides
Ø Soil erosion
5 (b) State three effects of air pollution on the physical environment. (3 marks)
Ø Dust particles in the atmosphere settles on leave surfaces blocking sunlight inhibiting photosynthesis.
Ø Excess production of carbon (IV) oxide which is a greenhouse gas blocks long wave terrestrial radiation increasing the atmospheric temperatures causing global warming.
Ø Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) gases react and deplete the ozone Layer which allows dangerous uv-radiation
Ø Gases emitted from some industries e.g. sulphur (IV) oxide and nitrogen (IV) oxide dissolve in air to form acid rain that causes withering of plants/kills animals
Ø Gases emitted from factories contain substances that corrode roofs of houses and metal structures
Ø Smoke and smog in the atmosphere reduce visibility which may lead to motor vehicle or aircraft accidents.
Ø Smoke and soot discolour vegetation, buildings and other structures.
Ø Smoke and soot particles cause a bad smell and discomfort and when inhaled they cause respiratory system diseases in Humans and animals.
Ø Some poisonous gases from industries may cause diseases and death of people.
SECTION B (75 marks)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
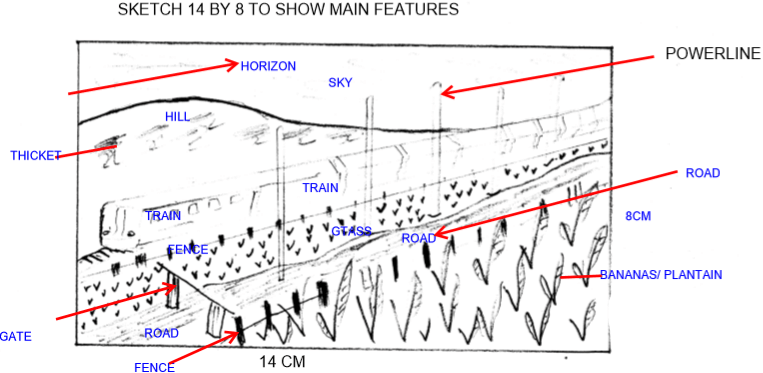
6 Study the following photograph and use it to answer Question 6( a ).

Ø Objects in the foreground are larger than those in the back ground
Ø Wider area has been captured/ focuses on many objects Ø There are perspective effect/ features progressively reduce in size from foreground to background
Ø Blurred skyline and horizon are properly captured
6a ii)Draw a rectangle 14 cm by 8 cm to represent the area of the photograph. On it, sketch and label the main features shown in the photograph. (6 marks)
6 (b) Explain four measures that African countries would undertake to solve the challenges associated with railway transport. (8 marks)
Ø Adopt new technology to track movement of trains to stop theft of goods
Ø African countries must agree to abolish old railway line and adopt 1meter standard gauge railway for easier transition of goods from one country to another
Ø Diversify the production of goods to allow the railway to transport more exported goods than imported goods
Ø Establish large standard warehouse for storing goods to ease the process of clearing and forwarding
Ø Improve security to curb vandalism of railway components
Ø Improve the roll on and roll off machines for faster handling of containers
Ø Reduce clearing and forwarding restrictions or conditions and various ports to reduce delay
Ø Set aside capital to construct dual rail lines which can be electrified for faster movement of goods
c) State five reasons why there is limited use of river transport in Africa
Ø Some rivers are very narrow for vessels to use
Ø Some rivers are shallow can only be used by small vessels Ø Some rivers have waterfalls and rapids hindering navigation
Ø Rivers are only found in specific places, not found in other areas
Ø Presence of other efficient and faster means of transport has taken focus way from river transport
Ø Some rivers have meanders inhibits movement of large vessels
Ø Some are border rivers therefore regarded as no-man’s-land no interest from other boarder states
Ø Some rivers are used for other more profitable economic activities like fishing, mining therefore navigation is rated secondary
Ø Most rivers have not been improved for navigation
6 d) Give four ways in which the use of mobile phones has contributed to the economy of Kenya. (4 marks)
Ø Has opened platforms for online trading
Ø Recharge on airtime and data bundles are taxed earning the country massive revenue
Ø It has boosted communication in emergencies saving lives like corona pandemic
Ø Imported phones are re-exported earning the country revenue
Ø It has created online jobs reducing unemployment
Ø It has boosted research and knowledge in agriculture boosting production
Ø Platforms like WhatsApp, telegram Instagram gas boosted national integration promoting peace for trade
Ø Online marketing of Kenyan natural resources and culture on YouTube has boosted tourism
7 (a) Give four physical conditions that favour sugarcane growing in the Lake Victoria basin. (4 marks)
Ø Well drained fertile soils /Black cotton soils
Ø Gently sloping/undulating landscape
Ø High rainfall 1200 to 1500 mm well distributed throughout the year
Ø Moderate high temperature/200C – 280C
Ø Long periods of night
7b (i) Describe the stages involved in the processing of sugarcane at the factory. (6 marks)
Ø Weighing of the cane,
Ø Washing to remove dirt
Ø Shredding/chopping of the cane
Ø Crushing of the cane in rollers to extract juice/ remove bagasse
Ø Filtering to remove solid particles and fine dark colored mud
Ø Liming, Boiling in evaporators
Ø Vacuum-panned to form massecuite
Ø Crystallization in open tanks
Ø Centrifuged to separate crystals from molasses Ø Refined to white sugar
Ø Grading
Ø Packing/bagging of sugar
7b (ii) Apart from sugar, give three other products obtained from sugarcane. (3 marks)
Ø Aconitic acid
Ø Bagasse
Ø Filter cake/mud
Ø Molasses
Ø Wax
7c Explain three causes for the decline of sugarcane farming in Kenya. (6 marks)
Ø Increasing population leading to land subdivisions lowering the acreage under sugarcane
Ø Competition from more profitable crops that takes short time for the available land space has made farmers pull out of cane farming
Ø Accidental fires/fires set by arsonists destroy the cane resulting in heavy losses to the farmers.
Ø Closure of some factories such as (Ramisi and Miwani) has deprived farmers of the source of income/annual closures factories for servicing of machines disrupts the farmers' calendar of activities.
Ø Delays in harvesting reduce the quality tonnage of the cane reducing the farmer's earnings.
Ø Flooding of market by cheap imported/sugar results in unfair competition causing delay in payments to the farmers.
Ø High cost of farm input reduces the farmer' profit margins Ø Mismanagement of factories and cooperatives leads to delayed payments thus discouraging the farmers
Ø Pests such as termites and white grub/diseases such as ratoon stunting and smut attack the plants and lowers the yields leading to low income for the farmers
Ø Narrow and impassable feeder roads in some areas leads to delayed delivery of the cane to the factory lowering the quality and subsequently the profit to the farmers.
Ø Prolonged droughts in some areas destroys the crop leading to huge losses
7d Explain three ways in which the Kenyan government is promoting the sugar industry. (6 marks)
Ø Enforcing the law to protect farmers from exploitation by brokers.
Ø Establishment of small scale out grower schemes for production and marketing of sugar.
Ø Financing research for high yielding cane. Subsidizing farm inputs to lower the cost of sugarcane production.
Ø Formation of Kenya Sugar Board to advice farmers on production and marketing of sugar.
Ø Giving financial assistance to revive the operations of the ailing sugar companies as was been done with Mumias sugar factory in August2017
Ø Restricting sugar imports to protect farmers from flooding the market with cheap imported sugar.
8a i) Define horticulture. (2 marks)
Ø Horticulture is the intensive cultivation of vegetables, fruits, flowers and ornamental plants for commercial purposes or it is export market oriented.
8a (ii) Outline five characteristics of horticultural farming in Kenya. (5 marks)
Ø Capital intensive or heavy capital invested to build green houses and buy inputs or install refrigerated facilities.
Ø Farms are generally small in size with few large ones.
Ø Horticulture farmers are highly specialized for high quality produce.
Ø Intensive use of land for maximum production.
Ø Involves advanced research, skilled labor and modem fanning methods for high quality and yields.
Ø Involves growing of flowers, vegetables and fruits.
Ø It is export market oriented and little is sold in the domestic market.
Ø Labor-intensive human labor needed.
Ø Located in areas with good and reliable transport network to markets and export points as the produce is highly perishable.
Ø Most horticulture farms are owned by rich individuals or foreign companies.
Ø Mostly done under greenhouses especially or flowers.
Ø Use of irrigation water or controlled water supply.
Ø Uses selected seeds and inputs for high production.
8b (i) Give four physical factors that favour horticultural farming in Kenya. (4 marks)
Ø Warm to hot/or moderate to high/temperatures
Ø Deep, well drained volcanic soils which support a variety of crops.
Ø Gently sloping or undulating land for easy construction of green houses.
Ø Moderate to high rainfall suitable for growth of fruits and vegetables.
Ø Availability of irrigation water from rivers and lakes enables crop cultivation throughout the year
8b (ii) Explain three challenges that horticultural farmers experience in marketing their produce. (6 marks)
Ø High freight charges by airlines which makes marketing of products expensive thus reducing profit margins.
Ø Control pests like aphids, termites has become a challenge since most are becoming resistant to drugs used Ø Diseases like late bright, rust, purple blotch, black rot and nematodes cause massive losses
Ø Farmers face competition from the established and upcoming producers which limits quantity sold to the world markets.
Ø High cost of inputs makes farmers fail to provide all that is required for production, reducing quantity and quality
Ø Inadequate refrigeration facilities lead to spoilage of produce hence wastage and loss.
Ø Low quality produce may be rejected in the world markets or get low prices making farmers incur heavy losses and get demoralized.
Ø Narrow, steep impassable road network during the rainy season makes the delivery of products difficult which is a loss to farmers.
Ø Persistent low world market prices leading to consistent low profit margins which discourages farmers.
Ø Stringent quality standards at the international markets increase the cost of production which lowers the profit margin.
Ø Substandard marketing strategies leads to exploitation of fanners by middle men which lowers farmers ‘profits.
8 c) You intend to carry out a field study in a nearby horticultural farm.
i)Apart from flowers, identify the other two types of crops you are likely to find in the farm. (2 marks)
Ø Fruits
Ø Vegetables
(ii) Give two sources of information that you would use for the field study. (2 marks )
Ø Atlas maps
Ø Horticultural Photographs
Ø Internet sites/electronic media on horticulture
Ø Journals/magazines on horticulture
Ø Microsoft Encarta
Ø Newspapers with horticultural articles
Ø Professionals/Geomorphologists/teachers
Ø Relevant geography text books
Ø School geography notes
Ø video documentaries on horticulture
Ø World encyclopedia
8c iii) State four factors that have contributed to fast growth of the flower farming sub-sector in Kenya. (4 marks) | Ø Availability of capital or loans or credit facilities invested by rich individuals or companies to start and expand horticulture farming.
Ø Availability of cheap human labor from the high population attracts many local and foreign investors.
Ø Availability of skills and trained extension workers who advice horticulture farmers on modem methods which has helped to expand the sector.
Ø Formation of Horticulture Co-operative Union, Horticulture Development Union and Horticulture Development Authority has helped give financial assistance and arrange marketing to the export markets
Ø Tarmacked roads, standard gauge railway network, airports for quick delivery of products to local and export markets.
9a (i) Differentiate between pelagic and demersal fish. (2 marks)
Ø Pelagic fish lives close to the water surface while demersal lives on ocean bed/deep waters
9a (ii) Describe the drift method of fishing. (6 marks)
Ø A large net stands vertically like a tennis net in seawater attachedtoa drifter ship or boat.
Ø It has floats on the upper side to keep it Floating in water. Ø It has weights on the lower side to make it sink and stand vertically below the water surface.
Ø The fish that try to swim through the net are trapped by their gills and cannot 1 move forward or backwards due to the small net mesh.
Ø After enough fish has been trapped the net is pulled by the drifter ship to the shore.
Ø The fish are removed from the net and taken for processing.
Ø The net is then returned back into the sea for more catch
9 b) Explain four reasons why there is widespread fresh water fishing in East Africa. (8 marks)
Ø Numerous inland fishing grounds such as lakes and rivers which are accessible to many people
Ø High demand for fresh water fish which makes fresh water fishing more popular while there is a low demand for salt or sea water fish,
Ø Narrow continental shelf and regular coastlines limit growth of plankton and fish breeding which limits the variety of edible fish.
Ø Stiff competition in the open sea from industrialized countries who use modem fishing equipment discourages local fisherman who thus prefer inland fisheries.
Ø Limited technology and inadequate capital make it difficult to develop marine fishing.
Ø Inland fisheries are rich in plankton and therefore have many edible fish species.
9 (c) (i) Explain how each of the following factors influence fishing in Kenya and Japan:
9c i) Market; (2 marks)
Ø Fish is perishable the amount of the catch per day is determined by demand and size of market fishermen can easily increase the catch if there is high demand and lower it when demand is low
Ø Large market with high demand will influence the type and quality of fishing equipment to be used by fishermen
Ø Large markets determine the extent to which deep sea fishing and inland fishing can be done small market may only explore shallow water/few lakes and rivers
9c ii) Technology. (2 marks)
Ø Use of radars to pinpoint/spot where shoals are, has increased efficiency and amount of the catch
Ø Self-contained vessels used in fishing has boosted the amount of the catch/freezing and processing Ø Technology has produced storm resistant vessels ensuring safety of fishermen, ensuring continuous fishing throughout the year
Ø Technology has also created quality fishing vessels that has increased the easiness to which deep seas have been exploited
Ø Technology has enabled comprehensive study of oceans and seas to understand fish breading patterns, movement, which has improved fishing patterns and catch
Ø Introduction of fish-cage farming technology in several lakes to complement fish pond farming
Ø Technology has eased demarcation of marine international territorial boundaries using global positioning system with has allowed smooth exploitation of international waters with minimal conflicts
9c(i)
(ii) State the significance of fishing to the economy of Kenya.
Ø Fishing creates self employment for individuals, reducing unemployment in the county/country
Ø Fishing has boosted development of port towns or fishing villages leading to urbanization,
Ø Fish products are raw materials for other industries promoting industrialization.
Ø Fishing activities promote the growth of related industries like net making or ship buildingand repair
Ø Fishing stimulates the development of roads opening up remote areas,
Ø Communication network in fishing villages have been boosted on markets and fishing grounds, boosting sales
Ø Fish products are exported which bring foreign exchange
Ø Sport fishing by tourists earns foreign currency to the government.
Ø Taxation of fishing activities gives revenuen to the government used to develop in other sectors of the economy.
Ø Fishing helps in the diversification of the economy which reduces over- reliance on agriculture.
10 (a) (i) Name two types of settlement patterns found in rural areas. (2 marks)
Ø Dispersed/ scattered pattern
Ø Nucleated pattern
Ø Linear pattern
Ø Radial pattern
10 (ii) State five factors that have contributed to the emergence of slums in urban centre (5 marks )
Ø Low incomeorunemployment.
Ø Shortage or lackofproperhouses.
Ø High cost of land, houses and high rental
Ø value in other parts of the town.
Ø Poor urban planningor corrupt officials.
Ø High rate of migrations into urban centres or rural-urban migrations.
10 (b) Explain four functions of Eldoret town. (8 marks)
Ø Commercial centre hub center for western counties
Ø Transportand communication centre, Eldoret international airport, terminus for Kenya Uganda railway,
Ø Residential centre of houses over 200000 people who live and work there
Ø Educational centre several universities Moi university, Eldoret university, Eldoret polytechnic
Ø Eldoret is and Agricultural collection distribution center where producers meet buyers form the rich agricultural hinterland of Usain Gishu
Ø Health centre or medical centre since it has Moi teaching and referral hospital, Mediheal and cancer center for east and central Africa
Ø Recreational center, tourist center the Usain Gishu plateau, Kerio valley, poa place
Ø Sporting center, it has the high attitude training center kip Keino stadium
Ø Eldoret Administrative centre since it’s the headquarter of Usain Gishu county
Ø Several industries like Raiply, Rivertex, kcc are all in Eldoret making it an Industrial centre
10 (c) State four factors that led to the growth of New York City in America. (4 marks)
Ø A fine natural rock basin for construction of port facilities.
Ø A rich large-hinterland of the U.S.A. and Canada provides raw materials for industries and goods for trade.
Ø Availability of fresh water from River Hudson for industrial and domestic uses.
Ø Deep water berths enable handling of large Vessels which make it one of the busiest sea ports in the world handling a large volume of trade.
Ø Tarmarked-8 lane-roads links to the rich interior hinterland, roads, railways, navigable river Hudson and canals for easy transportation of people and goods for trade.
Ø Ice free conditions due to the warm Gulf Stream current which melt water at the port in winter and make it operate throughout the year.
Ø Low tidal range enable ships to dock and leave the port easily promoting trade.
Ø The port links the New York City through the Transatlantic sea route to the world which made the town develop as a major sea port.
Ø The well sheltered islands with deep channels suitable for docking of ships/ islands provided suitable land for construction of settlements eg. Staten, Island, Long Island, Bronx Island Manhattan and Jersey Islands.
10 (d)Explain three measures that have been undertaken to reduce motor vehicle traffic congestion in Nairobi city. (6 marks
Ø By use of computerized street lights to regulate traffic flow, during peak hours
Ø Construction of overhead Nairobi express way and southern bypass for vehicle with no business at the city center this reduces the number of vehicles
Ø Creating separate lanes for bicycles and carts, this allows faster movement of vehicles
Ø Encouraging use public means by Restriction of personal cars from accessing central business district
Ø Raising of packing fees to discourage people accessing some parts of the city with personal cars
Ø Raising the price of fuel so that it becomes more expensive to use private cars
Ø Using flyover at junctions to eliminate intermittent flow of traffic
Ø Widening of road to eight lane which increases number of vehicles using the road at particular time