Published on April 29th 2024 | 16 mins , 3163 words
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
1. (a) List the two types of environment. (2 marks)
Ø Natural environment
Ø Human environment
(b) Explain how Geography is related to economics. (2 mks)
Geography focuses on the exploitation of resources, methods of their production, transportation of commodities and their consumption.
2. (a) Name two main indigenous breeds of beef cattle reared in Kenya. (2 marks)
Ø Zebu
Ø Boran
Ø Ankole Cattle
(b) State three ways in which government policy influences agriculture. (3 marks)
Ø Imposing quotas that control the importation of locally produced crops such as maize, wheat and sugarcane to protect local farmers.
Ø Offering subsidies and tax reliefs to lower the cost of production.
Ø Offering high prices for agricultural produce such as maize and wheat to encourage production.
Ø Signing trade agreements with foreign countries to expand/secure market for farm produce.
Ø Financing the establishment of large irrigation schemes to boost rain fed agriculture.
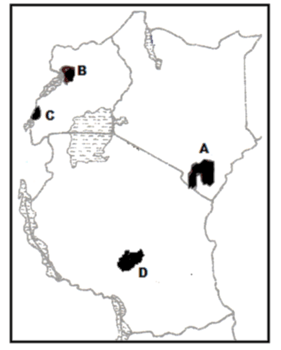
3. The diagram below some national parks in East Africa. Name the parks marked A, B, C and D. (4 marks)
Ø A – Tsavo
Ø B – Murchison fall
Ø C – Ruwenzori
Ø D – Ruaha
4. (a) Give two main projects through which land was reclaimed in the Netherlands. (2 marks)
Ø Zuider zee project
Ø Delta plan
(b) State four benefits that resulted in the reclamation of the Yala swamp in Kenya. (4 marks)
Ø Floods in the area were controlled
Ø Land for agriculture became available.
Ø Pests and waterborne diseases were controlled.
Ø Some people were settled in the created Bunyala scheme.
Ø Increased production of food such as rice thus increased income.
Ø Increased employment in the area.
Ø Roads in the area were improved thus opening up the area.
5. (a) State three physical factors favouring coffee farming in Brazil. (3 marks)
Ø South East Brazil experiences moderate to high temperatures (140C to 260C) which favours coffee growing.
Ø High rainfall of about 1500 mm received annually on the Brazilian plateau supports coffee growing.
Ø Deep, well drained, and porous Terra Rosa soil that is rich in potash and humus.
Ø Plenty of sunshine due to Brazil’s tropical location favours the ripening of coffee berries.
Ø Undulating land within the Brazilian Plateau enables the setting up of large plantations.
(b) Give three similarities between coffee farming in Kenya and in Brazil. (3 marks)
Ø Both countries produce Arabica coffee as the main coffee variety.
Ø Both countries produce coffee for both local and export markets.
Ø Both countries face stiff competition from other coffee producing countries.
Ø Both countries are affected by fluctuations in the world market prices for coffee.
Ø Both Kenya and Brazil market their coffee to the same countries
SECTION B
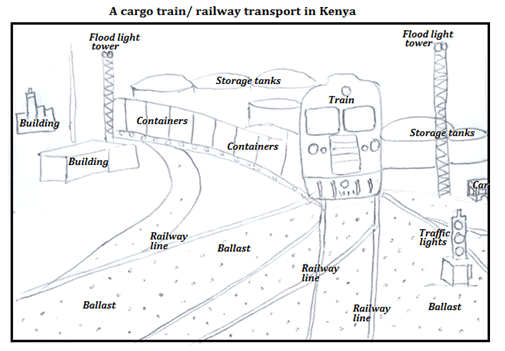
6. Study the photograph below and use it to answer the following questions.
(a) (i) Identify the type of photograph provided. (1 mark)
Ground general view
(ii) Give two reasons for your answer in (a)(i) above.(2 marks)
Ø The camera focuses on many objects.
Ø The horizon can be seen in the background.
Ø Objects become smaller in size from the foreground towards the background.
(iii) Identify the main activity shown on the photograph. (1 mark)
Railway transport.
(b) (i) Draw a rectangle 15 cm by 10 cm to represent the area covered by the photograph. (1 mark)
(c) (i) State five reasons why river transport is poorly developed in Africa. (5 marks)
Ø Some regions in Africa rugged forming steep slopes, rapids and waterfalls that hinder Navigation either upstream or downstream.
Ø Some rivers have very short navigable stretches thus uneconomical for transportation e.g. R. Senegal.
Ø Some rivers pass through unproductive areas thus uneconomical to develop river transport.
Ø Most rivers suffer seasonal fluctuation of water as most pass through regions receiving low rainfall.
Ø Situation especially at the river mouths and floods plains reduces the ideal depth for vessels.
Ø Some sections of river are shallow with fast flowing water which hinders smooth navigation e.g. R. Zambezi.
Ø Some sections of rivers have floating vegetation or swamps which hinder the movement of vessels.
Ø Some rivers have a high population of hippos and crocodiles which may topple some small boats thus endangering the passengers.
(ii) Explain five measures taken to solve transport and communication problems in Africa. (10 marks).
Ø Construction of Trans-Continental highways. African countries have agreed to construct highways to improve international
Ø Construction of international railways to connect land locked countries with sea ports e.g Ethiopia- Djibouti SGR, Tazara, (Zambia) with Dar-Er-Salaam
Ø Formation of regional trade blocks that encourage improvement of transport and communication within member countries such as COMESA and ECOWAS.
Ø Establishment of National airlines for effective air link among African countries e.g Kenya Airways, S. African Airways, and Air Uganda.
Ø Installation of wireless telephone and internet services which have improved communication between African countries.
Ø Connecting African countries with fiber optic cables to internet hubs which has improved internet connectivity and reduced costs.
Ø Liberalization of transport and communication sectors to involve private investors which has improved efficiency in the sectors.
Ø Peace mission through regional governments and the African Union are seeking peace through intervention in some countries. Through peace, transport and communication can be improved/ developed.
7. (a) (i) Define the term mining. (1 mark)
Mining refers to the process of extracting valuable minerals and fossils fuels on or from the earth’s crust.
(ii) Give four factors that influence the occurrence of minerals. (4 marks)
Ø Vulcanicity
Ø Metamorphism
Ø Weathering
Ø Leaching
Ø Erosion
Ø Sedimentation
Ø Evaporation
(b) Explain three ways in which mining activities cause pollution. (6 marks)
Ø Removal of vegetation to pave way for mining results in severe soil erosion which is a main cause of water pollution.
Ø Open cast mining produces a lot of dust which contributes to air pollution.
Ø Dumping of rock waste/overburden from open cast and underground mines results in land pollution.
Ø Mineral processing plants may discharge toxic effluent which pollutes water bodies such as rivers and lakes.
Ø Powerful explosives used to blast some hard rocks produces loud blasts that cause noise pollution.
(c) Describe the stages involved in gold processing in South Africa (6 marks)
Ø Gold bearing rock (ore) is brought to the surface from the deep mines and crushed into fine powder.
Ø The ground ore/fine powder is placed in a tank containing sodium cyanide solution.
Ø The sodium cyanide dissolves the gold particles forming sodium gold cyanide solution.
Ø Zinc powder is added to the sodium gold cyanide solution causing gold to precipitate.
Ø The gold precipitate is then separated from the cyanide solution in a filter process.
Ø Gold is then smelted in a furnace. Borax and soda ash are added to the molten gold to remove other less precious metals and impurities(refining)
Ø Pure gold obtained is then moulded into standard bars ready for sale.
(d) Explain four problems facing the gold mining industry in South Africa (8 marks)
Ø Cost of mining has increased due to deepening of the mines as South African gold mines are some of the deepest in the world.
Ø There is an increase in demand to provide higher wages leading to increased costs and frequent strikes that affect mining.
Ø Mines have become deep leading to problems of cooling, ventilation and pumping out excess flood water.
Ø Gold quality currently being mined is decreasing with deepening of the mines as compared to gold that was mined in previous years.
Ø Depletion of gold in the old mines results in high cost of exploring new sites.
Ø Shortage of skilled labour due to competition from other countries and sector of economy.
Ø Inadequate water supply for processing due to rapid urbanization and seasonal rainfall as gold requires a lot of water.
8. (a) What is unfavourable balance of payments?(2 marks)
Adverse/unfavourable balance of payment is a situation where the value of a country’s total exports (visible + invisible exports) is less than the value of its total imports (visible + invisible imports) thus a trade deficit.
(b) Name three major imports to Kenya from the Far East Asia. (3 marks)
Ø Motor Vehicles.
Ø Electronics
Ø Pharmaceuticals
Ø Industrial Machinery
Ø Clothes and foot wear.
Ø Vegetable oils
Ø Rice and Wheat.
Ø Iron and steel.
(c) Explain four benefits of international trade to Kenya. (8 marks)
Ø Kenya earns foreign exchange/currency through international trade. The hard currency is used in import trade.
Ø Trade generates revenue to the government through value added tax, tariffs customs duty charged at entry point for goods.
Ø Demand for goods both locally and internationally stimulates industrial growth as more industries are set up to produce the goods.
Ø Improvement in the transport sector such as railway, tarmac roads and international airports to facilitate the movement of goods in and out of the country.
Ø Trade has stimulated the exploitation of natural resources due to demand for certain goods from Kenya.
Ø Creation of employment opportunities in cargo clearing and forwarding/logistics activities to many Kenyans dealing in foreign trade.
Ø External trade has led to the development and expansion of towns such as Name, Lunga Lunga, Taveta and Mandera.
Ø Expansion of Agriculture as most trade items are Agricultural commodities.
Ø Trade has stimulated the development of activities such as banking, insurance and warehousing.
Ø External trade gives Kenyan consumers a wide variety of goods that are unavailable locally to satisfy their wants.
(d) (i) State four objectives of ECOWAS. (4 marks)
Ø To encourage trade among member states.
Ø To eliminate trade barriers on locally produced goods in the region.
Ø To promote free movement of goods and people in the region.
Ø To encourage the improvement of transport and communication in order to facilitate trade.
Ø To co-operate on matters on research in Agriculture forestry and industrial development
(ii) Explain four problems facing regional trading blocs in Africa. (8 marks)
Ø Some countries within the same trading bloc produce similar goods thus making the volume of trade to be low.
Ø Civil wars in some countries results to insecurity which negatively affects trade.
Ø Political differences among some leaders of member states have affected their co-operation.
Ø Free trade denies the importing countries the revenue they would have earned from customs duty/ levies.
Ø The flow of goods and services in the blocs is still slow due to poverty among the majority of the people in the regions.
Ø Poor transport and communication between member states slow the flow of goods and services.
Ø Different levels of industrialization makes some countries to rely on those that are more industrialized.
9. (a) (i) What is a Census? (2 marks)
A population census is the total process of collecting, compiling analyzing and publishing demographic, social and economic data pertaining all persons in a country at a specific time
Or
A census refers to the counting of the entire population of a country or area while compiling the social and economic information of the people
(ii) State four reasons why a census is important to Kenya (4 marks)
Ø A census provides information on the trends of mortality and fertility
Ø Information obtained helps governments to plan for the provision of basic facilities such as schools hospitals and food
Ø It helps in the creation of new administrative units such as counties, constituencies or wards
Ø It shows the composition of population in terms of age sex and regional distribution
Ø Total population assists the government to know if there are adequate resources
Ø A population census enables the estimation of population growth to determine literacy level.
(b)Explain four positive effects of high population growth to a country. (8 marks)
Ø Increased exploitation of natural resources that would otherwise remain underutilized/idle.
Ø There is a larger domestic market which promotes industrial development and expansion.
Ø Availability of cheap labour for large scale production thus cheaper goods.
Ø Increased innovation and creativity due to increased competition among citizens in various sectors.
Ø Increased urbanization thus development and expansion of basic facilities such as roads, power, water and social amenities
(c) Explain three causes of a reduced fertility rate in Kenya (6 marks)
Ø Increased rate of use of birth control measures among many productive females which lowers the number of children.
Ø More girls are attending school up to tertiary levels thus delaying in getting married which contributes to a lower fertility rate.
Ø Increased number of women mainly in urban centres opting to remain single thus opting to have very few children
Ø Modern career opportunities may delay young women from getting children as some employers avoid women who keep on going on maternity leave.
Ø Hard economic times in urban centres and the high cost of child upkeep have forced many people to limit the number of children which lowers the fertility rate.
(d) State five differences between Kenya’s population and that of Sweden. (5 marks)
Ø The birth rate in Kenya is high while in Sweden it is low
Ø The death rate in Kenya is relatively high while the death rate in Sweden is low
Ø Fertility rate in Kenya is high while fertility rate in Sweden is low
Ø Kenya’s population has a large number of young people below 20 years while Sweden’s population has a large number of mature and aged people / old people
Ø The population growth rate in Kenya is high while the population growth rate in Sweden is low
Ø Kenya’s population has a high dependency ratio while Sweden’s population has a low dependency ratio
10. (a) (i) Define the term urbanization. (2 marks)
The process through which a population is transformed from a rural-based agricultural life style to a modern commercial/industrial life style.
or
This is the process whereby an increasing number of the total population in a country settles in a place leading to the growth or expansion of towns.
(ii) List the three functional zones of an ideal urban centre. (3 marks)
Ø Central business district
Ø Industrial zone
Ø Residential zone
(b) Explain four physical factors that influence settlement. (8 marks)
Climate
Ø Areas that receive high rainfall attract many people as such support subsistence and commercial farming.
Ø Areas that receive low and very low rainfall attract very few people due to inadequate food and pasture.
Ø Regions that experience moderate to high temperatures have dense settlements.
Ø Areas that experience very high or very low temperatures are uncomfortable for humans, livestock and crops thus have very few settlements
Relief
Ø Gently sloping land is ideal for construction and crop farming thus attracts many settlements.
Ø Mountain tops and steep slopes are avoided/ have very few/no settlements due to difficulties in construction of houses and roads.
Ø Windward slopes are wetter thus attract dense settlements while leeward slopes are drier thus have fewer settlements.
Ø In temperate regions, slopes facing towards the equator are warmer thus have dense settlements.
Drainage
Ø Springs and rivers are provide clean water thus attract many settlements.
Ø Swamps and marshes harbor pests and hinder construction thus discouraging settlements.
Soils
Ø Deep and Well drained soils with a wide variety of mineral nutrients attract many settlements due to their high agricultural productivity.
Ø Infertile soils discourage settlements due to low agricultural productivity.
Availability of land
Ø Settlements can only be established where there is open space.
Ø Settlements can be concentrated in a specific area while the rest of land is reserved for economic activities such as large scale farming or grazing.
(c) Explain four factors that have led to the growth of Rotterdam as a large port. (8 marks)
Ø Rivers Rhine and Maas. Rotterdam is located at the mouth of rivers Rhine and Maas which are navigable to large parts of interior Europe thus easy access.
Ø Strategic location in Western Europe where sea routes converge from America, Africa and other parts of Europe gives Rotterdam and advantage over other European ports.
Ø Warm North Atlantic Drift Ocean current provides ice free conditions thus enabling the port to operate throughout the year.
Ø Its industrial function enables Rotterdam to receive a lot of raw materials and also deal in manufactured goods.
Ø New waterway consisting of Caland and Beer canals provided a deep harbor to handle many vessels.
Ø Construction of the Europoort which is an out port near the main entrance to handle very large ships that couldn’t reach the inner port areas greatly expanded the port.
Ø A large hinterland. Rotterdam serves a large hinterland in Western Europe such as Netherlands, Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg Switzerland and Austria thus handles transit goods.
(d) State four similarities in the functions of Nairobi and New York cities. (4 marks)
Ø Both cities are industrial centres with both light and heavy industry.
Ø Both cities are education centres with high schools colleges and universities.
Ø Both cities are international centres with Nairobi having UNEP and UN-HABITAT offices while New York is the headquarters of UNO, UNHCR and UN Security Council.
Ø Both cities are tourist centres with several attractions.
Ø Both cities are trade centres with securities exchange markets
Ø Both cities are transport and communication centres.