Published on January 18th 2026 | 8 mins , 1493 words
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
1. (a) State the characteristic of living organisms illustrated in the following diagram. (1 mark)
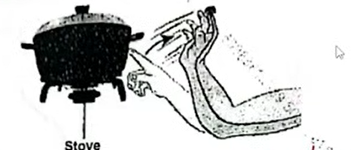
Irritability / response (to stimulus / stimuli) / living organisms respond to stimulus / stimuli / heat / temp (in their environment) Acc. Sensitivity
(b) State the significance of the illustrated characteristic to living organisms. (1 mark)
(Enables) living organisms move away from unfavourable conditions (of temp. / pressure / moisture) ; or converse.
2. Explain how relaxation of the diaphragm muscles leads to exhalation. (3 marks)
(Relaxing of the diaphram muscles) cause diaphragm assume a dome shape; reducing the volume of chest cavity; increasing pressure (hence expelling air out of the lungs / exhalation);
3. The following diagram illustrates an organelle obtained from a cell.
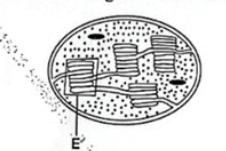
Chloroplast; acc plural
b) Name the part labelled E
Granum; acc grana
(c) Explain how the part labelled E is adapted to its function.
Packaged / organized in stacks / highly folded; to increase S.A. for packaging of (more) chlorophyll molecules (for absorption of more light / photosynthesis); Has (more) chlorophyll molecules; for trapping (more) light for photosynthesis;
The following diagram illustrates an organism belonging to a certain Class

(b) Suggest the likely habitat of the organism. (1 mark)
Aquatic / Water (environment) acc Example of water bodies
(c) State two reasons for your answer in (b). (2 marks)
Webbed feet / long legs for wading in water; (Curved) beak for filter feeding; Acc Modification alone, rej function alone, rej long legs alone acc. webbed feet alone.
5. (a) Name the type of muscle found in the following parts of the body:
(i) heart; (1 mark)
Cardiac (muscles);
(ii) Alimentary canal
Smooth (muscles);
(b) State two roles of the muscle named in (a)(ii).
Contract and relax to bring about movement of food down the alimentary canal / facilitate peristalsis ; contract and relax to facilitate mixing of food in the stomach / churning ; b is tied to (a)(ii)
The following diagram shows two organisms belonging to different Divisions
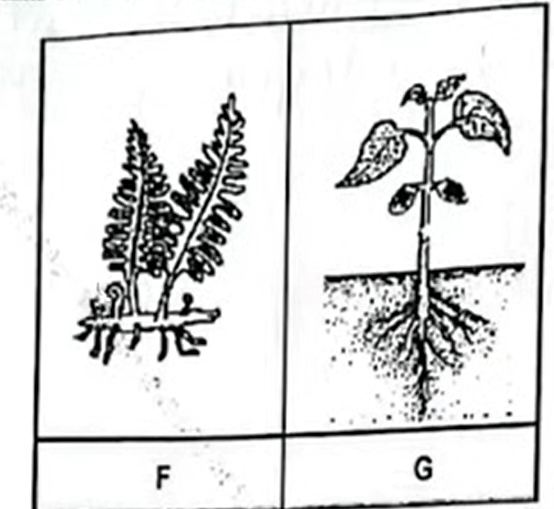
F - Pteridophyta ; rej wrong spelling (1 mark)
G - Spermatophyta ; (1 mark)
(b) Explain why organism G is considered more advanced than F. (2 marks)
Organism G produces seeds/fruits/flowers (which are more advanced reproductive structures than sori through which specimen F reproduces) ; specimen G has more advanced/developed transport/vascular (phloem and xylem) system (guaranteeing efficient water/nutrient movement and/or growth and survival) ;
9. Explain why sugary foods are harmful to teeth. (3 marks)
Bacteria (in the mouth) use sugar as (metabolic) substrates ; the metabolic waste products are acidic ; corrode tooth (enamel) ; forming cavities ; acc. formic / lactic / acetic acids ; Max 3
10. Form 3 students constructed the following food web for organisms in a certain ecosystem
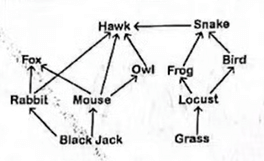
Hawk ;
(ii) construct a food chain ending with the organism named in a(i) as a tertiary consumer. (2 marks)
Black jack → mouse → owl → ; Hawk ;
(b) Name the mode of feeding exhibited by the snake. (1 mark)
Carnivorous ; rej Carnivore ;
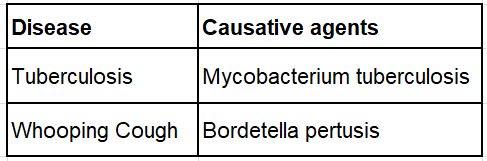
11. Complete the following table on respiratory diseases and their causative agents. (2 marks)
(a) (i) Name the feeding relationship illustrated in the photograph. (1 mark) Symbiosis ;
(ii) Explain your answer in (a)(i). (2 marks) Bacteria (in the root nodules) and (leguminous) plant benefit (mutually) from each other ; the bacteria fix nitrogen which is used by the plant ; the plant provides carbohydrates/shelter (to bacteria) a (ii) tied to a(i)
(b) Give one example of a similar feeding relationship in animals. (1 mark) Ruminant/mammalian stomachs and cellulase producing cellulose digesting bacteria / bees and flowers / oxpeckers and animals (cows/rhinos/zebras)
14. The following diagram illustrates a flower obtained from a certain plant.
(a) State the collective name given to the floral parts labelled M and N.
- M Pistil / Carpel / Gynoecium ; (1 mark)
- N Stamen / Androecium ; (1 mark) acc. Plural
(b) (i) Suggest the likely mode of pollination for the flower. (1 mark)
Insect pollinated ; acc Cross pollination ;
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (b)(i). (1 mark)
Large/conspicuous petals ; stigma positioned above anthers / heterostyly ; stigma located inside flower ; acc. converse
15. (a) Explain how low light intensity may bring about changes in the phenotype of some plants. (3 marks)
(Low light intensity) results in low photosynthetic rate/little amount of glucose/sugars manufactured ; making stems stretch for light/elongate/bend (towards) ; the stems/leaves may also be weaker/thinner/smaller leaves ; (and coloured) yellow ; (due to inadequate light) low light intensity may also lead to altered flowering
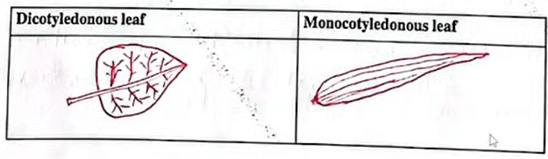
(b) Draw the diagrams to illustrate the difference between a dicotyledonous and a monocotyledonous leaf. (1 mark)
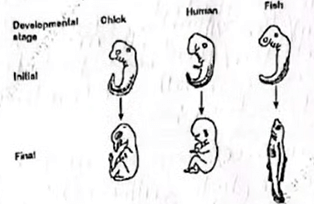
Comparative embryology ;
(b) Explain why the tail has been retained throughout the evolution of fish but not in humans and chicken. (2 marks)
Used for movement/propulsion/balancing ; whereas in chicken and humans it has no function/it is a vestigial structure ;
(c) State one other component likely to be common in the blood of the three organisms that implies they have a common origin. (1 mark) Presence of (some) serum protein structure / (plasma proteins (eg albumin / fibrinogen / globulin / prothrombin / antibodies) ; similar haemoglobin structure / blood group antigen ; presence of similar all organelles ; Protein sequence ; 1st one marked
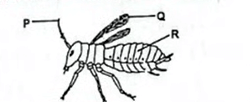
17. The following diagram illustrates an organism belonging to a certain Class.
(a) State how the parts labelled P, Q and R contribute to the success of the organism.
- P (Antenna) detect / sense for danger (for survival) / mate (for propagation of genes) harmful / favourable environmental condition (1 mark)
- Q (Wings) for flying / movement (in search of food / mates / favourable conditions / flee from danger) (1 mark)
- R (Abdomen) has spiracles for faster / efficient gaseous exchange (to facilitate respiration) ; (abdomen) has segments for reproduction ; (abdomen) contract and relax to enhance gaseous exchange ; (1 mark)
b) Account for the difference in the pattern of growth in a mouse and the organism illustrated. (2 marks) There is (smooth) continuous growth in the mouse while the illustrated organism / insect / arthropod there is intermittent growth pattern ; occasioned by presence of (hard) exoskeleton hinders continuous growth / growth takes place when the exoskeleton is shed ;
- Query successful
18. (a) Explain how spilling of oil in a fish pond affects the flow of energy in the pond. (3 marks) Covers water surface/clogs stomata; reducing uptake of CO2 (for photosynthesis); reduces penetration of light for submerged plants affecting rate of photosynthesis/ production of less oxygen (as a by product); resulting to reduce respiration/air circulation; less glucose/ sugars/food are produced, less energy released to the primary consumers and subsequent trophic levels.
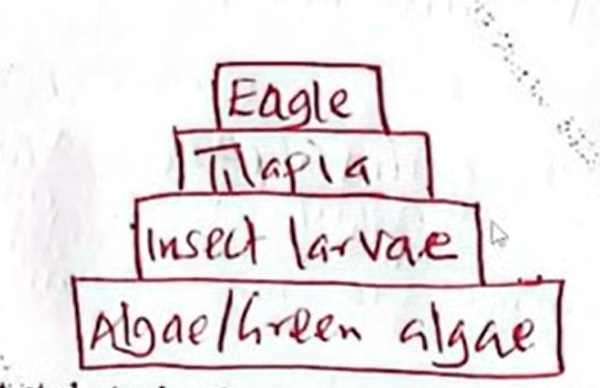
(b) The following organisms were found in a certain ecosystem.
Tilapia
Insect
larvae
Green algae
Eagle
Sketch a pyramid of numbers for the organisms in the ecosystem. (1 mark)
(a) State two processes that the students were investigating in the experiment. (2 marks)
Germination; respiration;
(b) State two observations that the students made after five days. (2 marks) Increase in temperature; emergence of plumule/radicle; acc. germination;
20. (a) Name the antigen and antibody present in the blood plasma of an individual with blood group A+. (2 marks) Antigen A/Rh/Rhesus factor; antibody b;
(b) Suggest the possible recipient of the individual's blood. (1 mark) AB+/A+ acc. AB/A rej. AB−/A−
21. (a) Name the physiological process that facilitates:
(i) uptake of water from the soil through the root hairs; (1 mark)
osmosis;
(ii) reabsorption of sodium ions from the kidney tubules. (1 mark)
Active transport;
(b) Explain why grass withers when it is continually sprayed with salty water. (3 marks)
The salty water is hypertonic to the cell sap in the grass; by osmosis; water molecules are drawn out of the grass/the grass lose water; grass cells become flaccid (and grass wither/dry up);
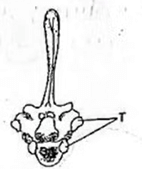
22. The following diagram illustrates a mammalian vertebra.
(a) Identify the type of vertebra illustrated. (1 mark)
Thoracic (vertebra);
(b) Name the bone that articulates with the vertebra at the parts labelled T. (1 mark)
Rib(s);
(c) Using observable features, explain how the vertebra is adapted to its function. (2 marks) Has long/extended neural spine / transverse process for muscle attachment; has neural canal / foramen for passage of blood vessels / neurons / spinal cord; Centrum / heartshaped to provide stability / support for thoracic cage; has facets / centrum for articulation (with other bones);